Whether you’re feeling a flat, down, looking for a boost or a remedy to a hectic lifestyle, Neuro-Linguistic Programming is full of practical tips and tricks which can help you to change and improve the way you view your life and how you live it.
>
>
Creating Well-Formed Outcomes in Your Life
You can drive yourself towards want you want to achieve effectively by assessing how your life is currently, and then begin deciding where you want to go and what you want to accomplish – the key to getting there is to weigh up all the aspects surrounding your life goals before settling on them. Follow these steps to get you started on the road to achieving your dream(s):
State your goal in positive terms.
What do I want?
Self-initiate and maintain your goal.
Am I doing this for myself or someone else?
Does my goal depend solely on me?
Ensure your goal is appropriately contextualised.
Where, when, how, and with whom do I want it?
Describe the evidence that will emerge from the procedure.
What will I be doing to get my goal?
How will I know I’m achieving it?
What will I see, hear, and feel when I have it?
Identify the resources you need.
What resources do I have now?
What resources do I need to acquire?
Have I got evidence of achieving my goal before?
What happens if I act ‘as if’ I already have it?
Check that your goal is ecological.
What is the real purpose behind why I want this goal?
What will I lose or gain if I have it?
What will and won’t happen if I get it?
What will and won’t happen if I don’t get it?
Describe the first step.
>
>
>
Reading the Eyes for Personal Insights
Eye movements can give subtle clues about what someone is thinking, feeling, or remembering. Everyone moves their eyes according to which internal mental system they’re using – recognising someone’s eye movement lets you know whether they are thinking in terms of images, sounds, or feelings and movement.
The table and image are based on looking at and assessing how someone’s eyes move in response to a question. In this instance we’ve taken what you would generally see for a right-handed person, if the person is left-handed these signals may be reversed.
| When someone is doing this | The eyes are doing this |
|---|---|
| Remembering a picture (Vr) | Move to the top left |
| Creating a picture (Vc) | Move to the top right |
| Remembering a sound or conversation (Ar) | Move horizontally to their left |
| Imagining what a sound will sound like (Ac) | Move horizontally to their right |
| Having a conversation with themselves (Ad) | Drop down and to their left |
| Accessing emotions (K) | Drop down and to their right |
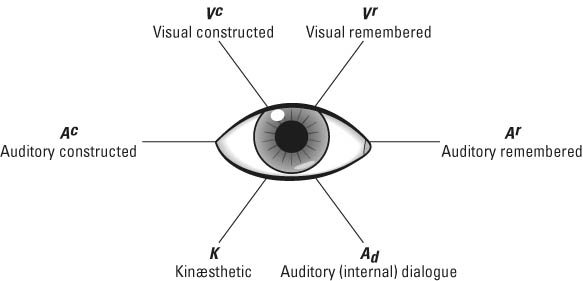
(N.B. Kinaesthetic means both movement and emotional experiences.)
>
>
>
Using Your Modalities and Submodalities
Everything you experience is as a result of information that you take in through your senses – visual (what you see), auditory (what you hear), kinaesthetic (touch and feelings), olfactory (smell), and gustatory (taste). These are known as modalities. Each modality has its own level of fine-tuning known as submodalities. For example, a picture can be bright or dull, black and white, or in colour; a sound can be loud or soft and so on.
Because submodalities are the basic building blocks of your experiences, they’re crucial tools in managing your mind and your emotions. You may find it useful to keep notes on how you can use submodalities to enhance the good areas in your life or change what isn’t working.
This can be done by assessing the submodalities in negative memories you have and appreciating the qualities of that memory. Being able to associate into and dissociate out of a memory gives you the power and control to understand the intensity behind any feelings you have in response to that situation. Looking at these memories of situations and/or people in an objective, calm and collected way, you can make great personal progress to overcome or just deal better with things that challenge you.
>
>
>
How to Squash Your Limiting Beliefs
Limiting beliefs are those negative little thoughts or judgements that prevent you from being your best self, such as ‘I can’t make friends easily’ or ‘People generally aren’t very nice’. Follow these steps to squash those limiting beliefs and replace them with helpful constructive opinions. This way you can end up seeing them in a different and more positive light.
Think of a limiting belief that you have and make a note of the picture that comes to mind.
Think of a belief that you no longer find true.
This can go along the lines of, ‘I used to believe in Santa’. Look at the picture that is presented by this belief that is no longer true.
Think of a belief that, for you, is an absolute certainty.
Need help? Think of the stars when you’re sitting in a brightly lit metropolis. Even though you can’t see them close to, you know the stars exist and you know the sun will rise in the morning. Then picture the sun rising, or whatever belief you choose.
Think of a belief you’d rather have than the limiting belief you picture in Step 1.
This may be the opposite of your limiting belief, just stated in the positive. ‘I can be fit, healthy, and weigh 140 pounds again.’ And then notice the picture that accompanies your new belief.
Change the submodalities of the limiting belief from Step 1 into those of the belief that is no longer true for you in Step 2.
Change the submodalities of the belief you would rather have from Step 4 into those of the belief which you are absolutely certain of from Step 3.
>
>
>
Remembering the NLP Presuppositions
Neuro-Linguistic Programming provides some basic positive assumptions and constructive convictions about the world. A few are listed here, take a look and try playing with these in your mind to see if any of them speak to you.
The map is not the territory.
People respond according to their map of the territory.
There’s no failure – only feedback.
The meaning of the message is the response it draws out.
If what you’re doing isn’t working, do something different.
The person with the most flexibility influences the outcome of any interaction.
You cannot not communicate.
You already have all the resources you need to achieve your desired outcomes.
Every behaviour has a positive intent.
People are much more than their behaviour.
The mind and body are interlinked and affect each other.
Having choice is better than not having choice.
Modelling successful performance leads to excellence.
>
>
dummies
Source:http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/nlp-workbook-for-dummies-cheat-sheet-uk-edition.html
No comments:
Post a Comment