Rosaceae is the third-largest plant family. This family includes many ornamental landscape plants, fruits, and berries, including apples, cherries, raspberries, and pyracantha, characterized by the shape of the hypanthium (the part of the flower where the seeds develop) and by petals in groups of five. Roses are members of the plant genus Rosa. Within that genus, roses are grouped into classifications based on the characteristics that each particular plant displays.
Your choice of rose depends on how you plan to use it and on your personal preferences. Some rose gardeners grow only one or two types of roses, and others grow many types. Try growing one or two in each class and see which rose types you prefer.
The following list shows you the basic differences among the various types of roses.
- Hybrid teas: These roses bear large flowers that commonly grow one to a long stem and bloom continually throughout the growing season. The bush can grow quite tall, with an upright habit (a term rosarians use to describe the shape or look of a plant). Hybrid tea roses are usually budded onto a vigorous rootstock, and are a great choice if you like large flowers with a pleasant rose form and if you like to make rose arrangements or have cut flowers in the house.
- Grandifloras: These are upright plants with hybrid tea-type flowers. The flowers often grow in clusters, but the stems on each flower within a cluster are long enough for cutting. Grandifloras normally grow to between 3 and 6 feet tall. They're almost always budded and are a good choice if you like lots of blooms for color in the garden and stems for cutting, all on the same plant.
- Polyanthas: A forerunner of modern floribundas, the plant itself can be quite large, covered with small flowers. Their usual habit is compact, hardy, and generous-blooming. The variety you see most often is 'The Fairy' — a wonderful variety, covered with small pink flowers on a plant that can spread to several feet in height and width.
- Floribundas: These plants have flowers that are smaller than hybrid teas and which grow in clusters on short stems. The bush is usually quite compact and blooms continually throughout the growing season. Most floribundas are budded, but commercial growers are beginning to grow them on their own roots. Choose floribundas if you need fairly low-growing plants that produce great numbers of colorful flowers.
- Miniatures: Extremely popular small plants, miniatures are usually between 6 and 36 inches in height, with their leaves and flowers in perfect proportion. They customarily grow on their own roots, and aren't budded, which makes them hardier in cold climates. Most mini varieties bloom profusely throughout the growing season and are a great choice for lots of color in a small space. You also can grow miniatures indoors in pots under a full-spectrum fluorescent light or grow light. Merely putting them on a windowsill won't work—they won't get enough light to thrive and blossom.
- Recently, the American Rose Society classified roses thought to be too large to be miniatures and too small to be floribundas as "mini-floras." The name hasn't yet been completely accepted by nursery workers, so these varieties are grouped as miniatures.
- Climbers: These plants don't really climb like clematis or other true vines that wrap around or attach themselves to supports. They do, however, produce really long canes that need to be anchored to a fence, trellis, or other support. Otherwise, the plants sprawl on the ground. Flowers bloom along the whole length of the cane, especially if the cane is tied horizontally, such as along a fence. Some climbers bloom only once in the spring, but many modern climbers produce flowers throughout the growing season.
- Shrubs: Because most are quite hardy and easy to grow, and great for landscaping, shrubs have become very popular in recent years. They're generally large plants, and most, particularly the modern shrubs, bloom profusely throughout the season. If you want to fill a large space with color, the shrub category offers a great many choices.
- Old garden roses: Often referred to as Antique roses, these roses were discovered or hybridized before 1867. The classification "old garden roses" is made up of many subclasses of roses, including alba, bourbon, China, hybrid perpetual, damask, and the species roses. Many old garden roses bloom only once during the growing season. Old garden rose aficionados enjoy the history and study of these lovely and often fragrant plants.
- Tree roses, or standards: These aren't included among the basic categories because nearly any rose that is grafted (or budded) onto a tall trunk is a tree rose. Most often, hybrid teas, floribundas, and miniatures are used as tree roses. These plants really aren't even trees. Most just have that lollipop tree look, as shown in Figure 1, but are only 2 to 6 feet high. They're wonderful either in the ground or in containers but are very susceptible to winter damage, and in cold climates, you must either bury the entire plant in the ground or bring it into a cool garage.
>
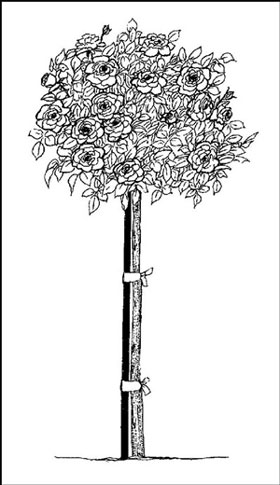
Figure 1: A rose trained to grow as a "tree rose" or "standard."
When you go to a garden center to choose your rosebushes, knowing which classification of rose you want is important. The classification gives you hints about how you can use it in your garden. The variety you choose depends on your personal preference as to color, hardiness, and so on. You don't want to plant a once-blooming old garden rose in a spot where having season-long color is important.
>
dummies
Source:http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/identifying-rose-classifications.html
No comments:
Post a Comment