A video game is more than the sum of its pieces; a game has a synergy that, after the game is complete, makes it something unique. Creating this synergy takes a lot of technical know-how, as well as a sense of design and art. Basically, you need to be a Leonardo da Vinci and an Albert Einstein all in one.
The basic sequence of game design is as follows:
- Come up with an idea for a game.
- Create storyboards and rough sketches of your game world, the main characters, and the action.
- List the details of your game and take into consideration everything about the game "universe."
- Finally, put these concepts all together into a design document, something like a movie script that contains everything about your game.
Developing an idea
Before you write a game, you need an idea — a story, something to start with. Brainstorm and come up with an idea for a game; the idea should be loosely based on something that has at least a fleeting resemblance to a story. Then you need to come up with the goals of the game. Ask yourself questions such as "What will the player do?" and "How will the player do it?"
Maybe you're wondering, "Where do I get ideas for games?" Well, you can't tap into any magical formulas, but you can look in a few places:
- Other games: Don't copy another game, of course, but improving and taking a new perspective within the game is fine.
- Movies and videos: Watch as many sci-fi movies as possible and see if you can come up with a game based on some of their ideas and content. Of course, you need to get permission from the filmmaker if you use any characters or story lines from those movies.
- Real-life games: You can take a game such as hockey and make a computer version of it, or make a futuristic version of it.
- Dreams and nightmares: This technique is a gold mine; in your mind, you can try anything out. Go to sleep thinking about games, demons, monsters, or whatever, and hopefully, you will have a killer dream that gives you an idea for a game.
After you have your game ideas, then you need to outline the story.
Storyboarding
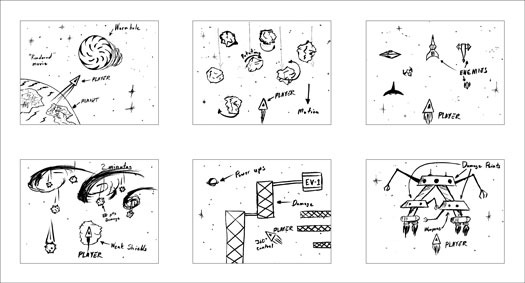
One of the best ways to see a game is to storyboard it — to create a sequence of drawings that show the levels of the game or the different scenes and goals. Each storyboard should include a paragraph or two to describe what is going on. Figure 1 depicts a basic storyboard for an imaginary shoot-'em-up game.
>
>
Figure 1: A typical game storyboard.
As you can see, the storyboard has six frames; each frame represents a different level of the game, and the final frame is the goal. Notice that the storyboards are sketched and messy. Storyboard sketches are used only for brainstorming and for getting down on paper the general flow of the game.
Considering the details
After you create storyboards, you write the details of the game design. This stage is where the process gets complex. You have to think of every possible detail and write something about it — because when you make your game, you are a god — well, at least a demigod. If you don't program a specific detail, it's not going to happen.
You need to figure out all the rules and the structure of the game. For example, here's a list of questions to consider:
- What can the game character do? Can he or she fly, swim, and teleport?
- How many different enemies will the hero fight?
- What kind(s) of weapons are available?
- How does the player get rejuvenated?
- Can more than one player play at once? If so, what are the ramifications of this?
- Will the game's perspective be a side view, top view, or first-person and full 3-D view?
- What kind of sound track? Rock, rap, techno?
- What is the personality of the main character?
These examples are just some of the details you need to think about. The key here is to create the characters, rules, laws, and goals of your game universe in as much detail as possible. That's necessary because you're going to generate the artificial universe they all exist in. The more detail you include, the better the game will be.
Constructing a design document
After you have all the storyboards and details of the game written down, create a design document. The goal of the document is to record all your ideas in a format that resembles a movie script. Creating the document is a housekeeping step, but it gives you another chance to change your mind, see if some rule or event is totally stupid, or add another game element.
The result of developing the design document is that your imaginary world becomes more vivid in your mind. When you start talking to yourself about the stuff that is happening in your game, when your imaginary world is so thick with texture and so alive with detail that you can see it, then writing a game around it is much easier, because you aren't making things up as you go. Having a clear picture of a game's world is one of the most important issues in game design.
The universe you create must be coherent; it must be well thought out enough to hang together about as well as the universe we live in (or better). If your game universe is coherent, the players will lose themselves in it; they will experience a suspension of disbelief and really have fun. On the other hand, if you come up with a half-baked idea and then wing it as you go, your game ends up looking thrown together, which doesn't invite belief. Without thought or planning, you won't pull the players into your world, and they won't play your game!
After you have a design document in hand, you're in a far better position to create a solid game. As you work on the game, you won't be tempted to impulsively add elements that are inappropriate or out of place in your game's world.
Don't misunderstand. Changing and adding to your design is acceptable, but make sure all the elements work well together. If players aren't distracted by inconsistencies in your game's universe, they can be fully involved with the characters and situations.
>
dummies
Source:http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/designing-video-games.html