In dabbling in quantum physics, you come across spin operators and commutation relationships, and many formulae, principles, and effects named for people such as the Hamiltonian, the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, the Schrödinger Equation, and the Compton Effect.
>
>
Quantum Physics and the Hamiltonian
One of the central problems of quantum mechanics is to calculate the energy levels of a system. The energy operator, called the Hamiltonian, abbreviated H, gives you the total energy. Finding the energy levels of a system breaks down to finding the eigenvalues of the problem
The same equation in matrix terms looks like this:
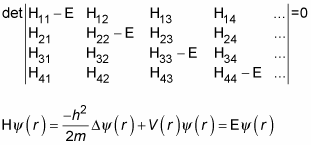
>
>
>
Quantum Physics and the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
In quantum physics, you encounter the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, which says that the better you know the position of a particle, the less you know the momentum, and vice versa. In the x direction, for example, that looks like this:
where Dx is the measurement uncertainty in the particle’s x position, Dpx is its measurement uncertainty in its momentum in the x direction, and
This relation holds for all three dimensions:
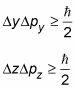
>
>
>
Quantum Physics and the Schrödinger Equation
In quantum physics, the Schrödinger equation describes the energies and probable locations of electrons. Much of quantum physics is largely about solving this differential equation for a variety of potentials, V(r):
The Schrödinger equation work in three dimensions as well:
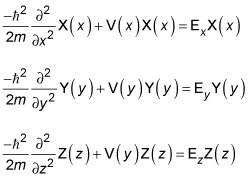
>
>
>
Spin Operators and Commutation in Quantum Physics
Don’t think quantum physics is devoid of anything but dry science. The fact is that it’s full of relationships, they’re just commutation relationships — which are pretty dry science after all. In any case, among the angular momentum operators Lx, Ly, and Lz, are these commutation relations:

All the orbital angular momentum operators, such as Lx, Ly, and Lz, have analogous spin operators: Sx, Sy, and Sz. And the commutation relations work the same way for spin:
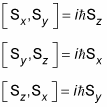
>
>
>
Quantum Physics and the Compton Effect
In quantum physics, you may deal with the Compton effect of X-ray and gamma ray qualities in matter. To calculate these effects, use the following formula, which assumes that the light is represented by a photon with energy E = hu and that its momentum is p = E/c:

>
>
dummies
Source:http://ca.dummies.com/how-to/content/quantum-physics-for-dummies-cheat-sheet.html
No comments:
Post a Comment