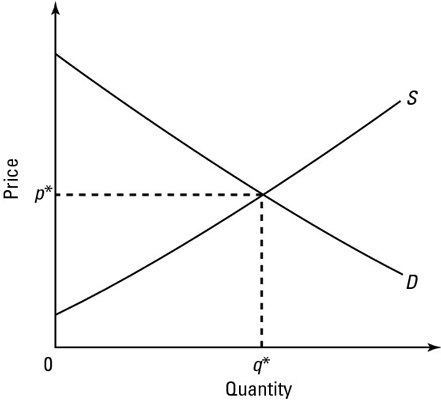
Buyers and sellers interact in markets. The market equilibrium price, p*, and equilibrium quantity, q*, are determined by where the demand curve of the buyers, D, crosses the supply curve of the sellers, S.
In the absence of externalities (costs or benefits that fall on persons not directly involved in an activity), the market equilibrium quantity, q*, is also the socially optimal output level. For each unit from 0 up to q*, the demand curve is above the supply curve, meaning that people are willing to pay more to buy those units than they cost to produce. There are gains from producing and then consuming those units.
dummies
Source:http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/what-is-market-equilibrium.html
No comments:
Post a Comment