Even though each of the Microsoft Office 2007 Suite applications does something different, they all have a few things in common. The Office 2007 program will go more smoothly and save you time if you learn some necessary commands and how to recover from a computer crash or a power failure.
>
>
Essential Office 2007 Commands
You can make running your Office 2007 program easier if you use these simple shortcuts. These commands, such as undoing a mistake and zooming in and out will help you save time.

Entering symbols: To enter a symbol or foreign character that isn’t on your keyboard, go to the Insert tab and click the Symbol button. Then make a choice in the Symbol dialog box.
Identifying yourself: Throughout the Office programs, you can enter your name, initials, and sometimes your address automatically on notes, revision marks, comments, address dialog boxes, and other places. To make sure that Office knows who you are and can enter your personal information automatically, click the Office button and choose [Application] Options on the drop-down list. Then, in the Personalize section of the Options dialog box, enter your name and initials.
>
>
>
AutoRecovering from a Power or Computer Failure in Office 2007
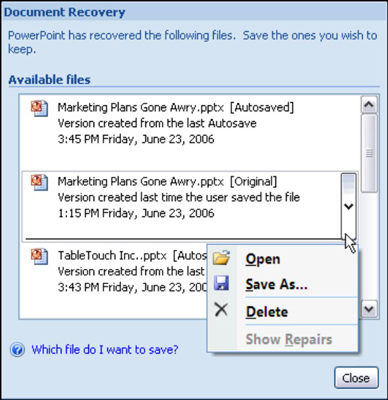
Say you’re working in an Office 2007 program and the power goes out or your computer dies. Once you get your computer restarted and re-open the program, the Document Recovery task pane appears with a list of files you had open when the crash happened:
AutoSaved files are files that Office saves as part of its AutoRecovery procedure.
Original files are files that you save by clicking the Save button.
The Document Recovery task pane tells you when each file was saved. By studying the time listings, you can tell which version of a file — the AutoRecovery file or the file you saved — is most up to date.
Open the drop-down list for a file and choose one of these options:
Open: Opens the file so that you can examine it. If you want to keep it, click the Save button.
Save As: Opens the Save As dialog box so that you can save the file under a different name. Choose this command to keep a copy of the recovered file on hand in case you need it.
Delete: Deletes the AutoRecovery file. (This command is available with AutoRecovery files, not files that you save on your own.)
Show Repairs: Shows repairs made to the file as part of the AutoRecovery procedure.
>
>
dummies
Source:http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/office-2007-allinone-for-dummies-cheat-sheet.html
No comments:
Post a Comment